Although Montana midwives had a long history of working with doctors to serve the needs of women in their communities, their profession—and especially the idea of home birth—faded from mainstream acceptance as the hospital replaced the home as the “normal” birthing location. By the 1950s, a majority of women across the United States delivered their babies in hospitals. Even as hospital births became more common, midwives continued to assume that pregnancy and delivery were nonmedical events. Physicians, on the other hand, began to insist that medical assistance and access to technology were necessary for safe deliveries.
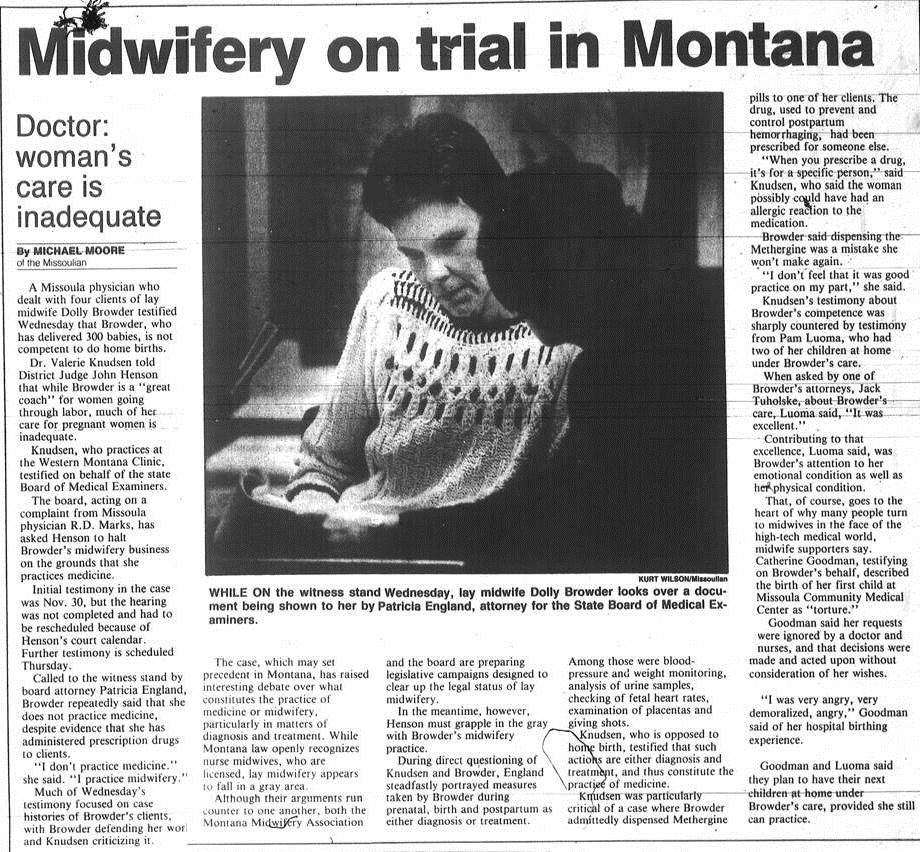
The conflict crystalized in 1988 when the Montana Board of Medical Examiners, at the request of a Missoula physician, pressed charges against a Montana midwife, Dolly Browder, and initiated a court case, accusing her of violating the Medical Practice Act by practicing medicine without a license.
After a three-day civil trial, the Missoula judge ruled against Browder. He concluded that she was practicing medicine and banned her from assisting pregnant women. The case concluded in January 1989, just as the Fifty-first session of the Montana legislature convened. With the looming threat of additional lawsuits, the Montana Midwifery Association hired a lobbyist, raised funds, and organized supporters. Their goal: To change the Montana Medical Practice Act to exempt home birth midwifery. Continue reading Legalized Midwifery: Montana Leads the Way