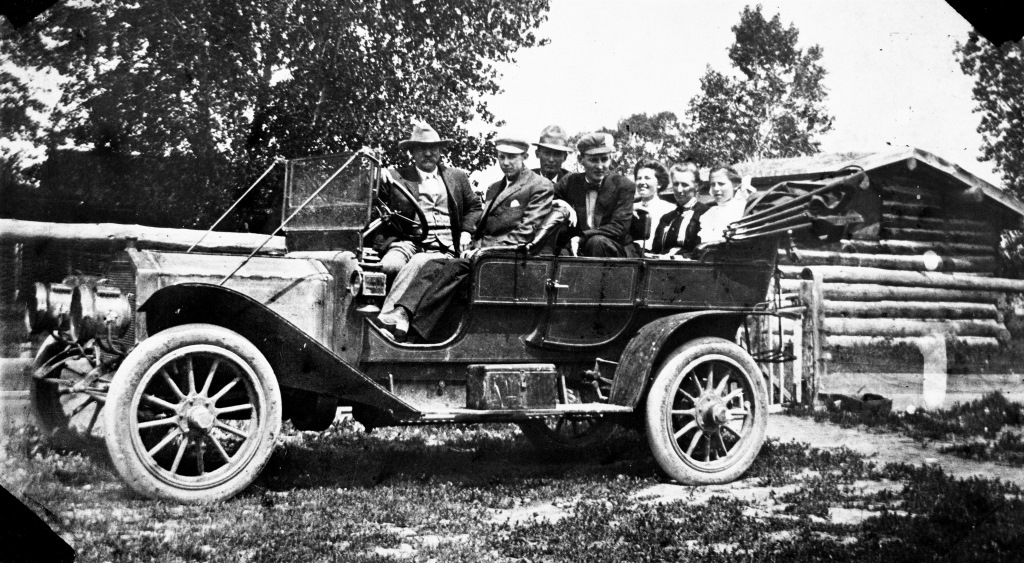
In late August and early September of 1927, Daniel Slayton, a Lavina, Montana, businessman and farmer, lay dying of bone cancer. During the final three weeks of his life, he spent no moment alone. Daughters, daughters-in-law, his cousin Mary, the community midwife, a nurse hired from Billings, and Slayton’s wife, Lizzie, cared for him and kept vigil. Though Slayton’s adult sons had earlier helped him seek treatment and, in the end, came to say their goodbyes, the women in his life mostly watched over him in his final hours.
In serving as family caregivers, Montana women have joined a legion of women across time. Before 1900, hospitals typically cared for soldiers, the poor, and the homeless. On Montana’s frontier, where single men far outnumbered women, churches underwrote Montana’s earliest hospitals. Soon self-supporting matrons converted boardinghouses into private hospitals. In the first half of the twentieth century, Montana pest houses, poor farms, and finally, state institutions such as the Montana State Tuberculosis Sanatorium at Galen provided some long-term care for Montanans without families. Nevertheless, a family’s women—its mothers, wives, sisters, aunts, daughters, and cousins—typically assumed responsibility for the care of relatives. Into the 1960s, and beyond, women performed this work out of necessity, longstanding tradition, and often love. Continue reading The Watchers: Montana Women Care for the Sick and Dying